Understanding vitamin K and its crucial role in the human body is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing potentially serious medical conditions. Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a critical part in blood clotting, bone metabolism, and preventing excessive bleeding.
What is Vitamin K?
Vitamin K exists in two primary forms: vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) and vitamin K2 (menaquinone). These vitamins are fundamental to several bodily processes, with the most important being blood coagulation. Unlike some other vitamins, vitamin K helps activate proteins that are essential for blood clotting, preventing uncontrolled bleeding.
The human body requires vitamin K to produce prothrombin, a protein directly involved in blood clotting. Without adequate vitamin K, individuals can experience significant health risks, including prolonged bleeding and potential hemorrhagic complications.
Symptoms of Vitamin K Deficiency
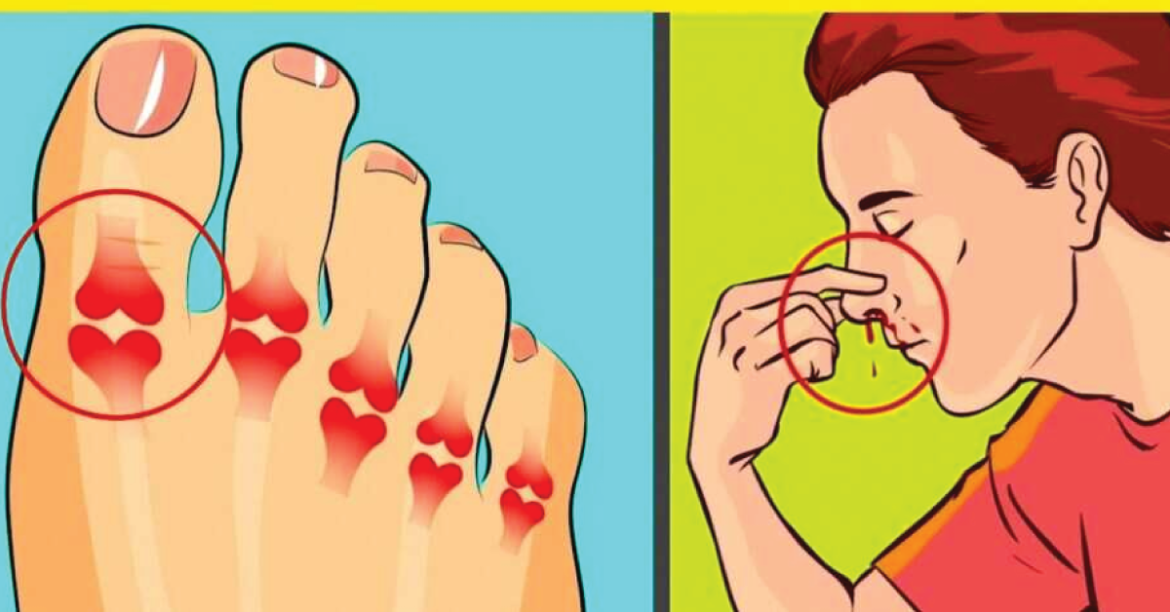
Recognizing vitamin K deficiency early is crucial for preventing serious health issues. Common symptoms include:
- Easy bruising
- Excessive bleeding from minor wounds
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Blood in urine or stool
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
In newborns, vitamin K deficiency can be particularly dangerous, potentially leading to Vitamin K Deficiency Bleeding (VKDB), which can cause intracranial hemorrhage and other life-threatening conditions.
Causes of Vitamin K Deficiency
Several factors can contribute to vitamin K deficiency:
- Inadequate dietary intake
- Malabsorption disorders
- Chronic liver disease
- Prolonged antibiotic use
- Certain medications that interfere with vitamin K absorption
Newborns are especially vulnerable due to limited vitamin K transfer from mother to child and low levels in breast milk.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Medical professionals diagnose vitamin K deficiency through blood tests measuring prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR). These tests assess the blood’s ability to clot effectively.
Treatment typically involves:
- Vitamin K supplements
- Dietary modifications
- Vitamin K injections for severe cases
- Addressing underlying health conditions
Vitamin K-Rich Foods
Preventing vitamin K deficiency can be achieved through a balanced diet featuring foods high in this essential nutrient:
- Leafy green vegetables (kale, spinach, collard greens)
- Fermented foods
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Vegetable oils
Prevention Strategies
To minimize the risk of vitamin K deficiency, consider these preventive measures:
- Consume a balanced diet rich in vitamin K
- Consider supplements if recommended by a healthcare professional
- Monitor any medications that might interfere with vitamin K absorption
- Ensure newborns receive vitamin K injections
Conclusion
Vitamin K is a critical nutrient essential for blood clotting and overall health. By understanding its importance, recognizing potential deficiency symptoms, and maintaining a balanced diet, individuals can effectively manage their vitamin K levels and prevent potential complications.
Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized medical advice, especially if you suspect a vitamin K deficiency or have underlying health conditions that might impact nutrient absorption.