Vitamin B12 is a vital nutrient that is often overlooked, despite its importance for maintaining overall health. This essential vitamin plays a key role in the metabolism of cells, and its deficiency can lead to long-term health conditions, including neurological disorders. Understanding the early warning signs of a B12 deficiency is crucial to prevent potential health issues.
In this post, we’ll explore the significance of vitamin B12 for your health and highlight the foods that are excellent sources of this nutrient. Below are some of the key benefits of vitamin B12:
1. Enhances Digestion
Vitamin B12 supports the production of digestive enzymes, which help break down food and maintain a healthy metabolism. It encourages the growth of beneficial gut bacteria while eliminating harmful bacteria, thus promoting a balanced digestive system. This helps in the prevention of digestive issues such as inflammatory bowel disease and Candida infections.
2. Protects Nerves from Damage
The myelin sheath, a protective layer surrounding nerves, shields them from toxins and damage caused by free radicals. Without adequate vitamin B12, this protective layer can deteriorate, leading to nerve damage. When nerves are compromised, the transmission of signals between the brain and body is disrupted, increasing the risk of nerve-related conditions.
3. Reduces Risk of Heart Disease and Stroke
Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death in the U.S. Studies have shown that elevated levels of homocysteine—a non-protein amino acid—are a greater risk factor for heart disease than cholesterol. Low vitamin B12 levels can cause an increase in homocysteine, which triggers inflammation and heightens the risk of heart disease and stroke. By maintaining sufficient B12 levels, you can help keep homocysteine in check.
Read more: Beetroot Juice – A Natural Solution for Enhancing Heart Health and Reducing High Blood Pressure
4. Boosts Energy Levels
Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in energy production by helping convert carbohydrates into glucose, which fuels your body. Without enough B12, cells become starved for energy, leading to fatigue and weakness. Maintaining adequate levels of this vitamin is essential for staying energized throughout the day.
5. Supports Bone Health
People with osteoporosis and similar bone conditions often have elevated homocysteine levels. Since vitamin B12 helps lower homocysteine, it may be especially beneficial for individuals dealing with bone health issues.
6. Prevents Anemia and Supports Red Blood Cell Production
Vitamin B12 is vital for the production of red blood cells (erythrocytes). Its deficiency can lead to megaloblastic anemia, characterized by weakness and chronic fatigue.
Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
1. Muscle Weakness
A lack of oxygen in muscle cells due to B12 deficiency can result in muscle weakness. If you find it difficult to carry out simple tasks like lifting a bag, it may be a sign that your muscles are not receiving adequate oxygen.
2. Eye Issues
A prolonged B12 deficiency can damage the optic nerve, leading to vision problems such as blurred or double vision, light sensitivity, or even partial vision loss.
3. Dizziness
Frequent episodes of dizziness or lightheadedness, particularly when standing or moving quickly, can be an indication of low vitamin B12 levels.
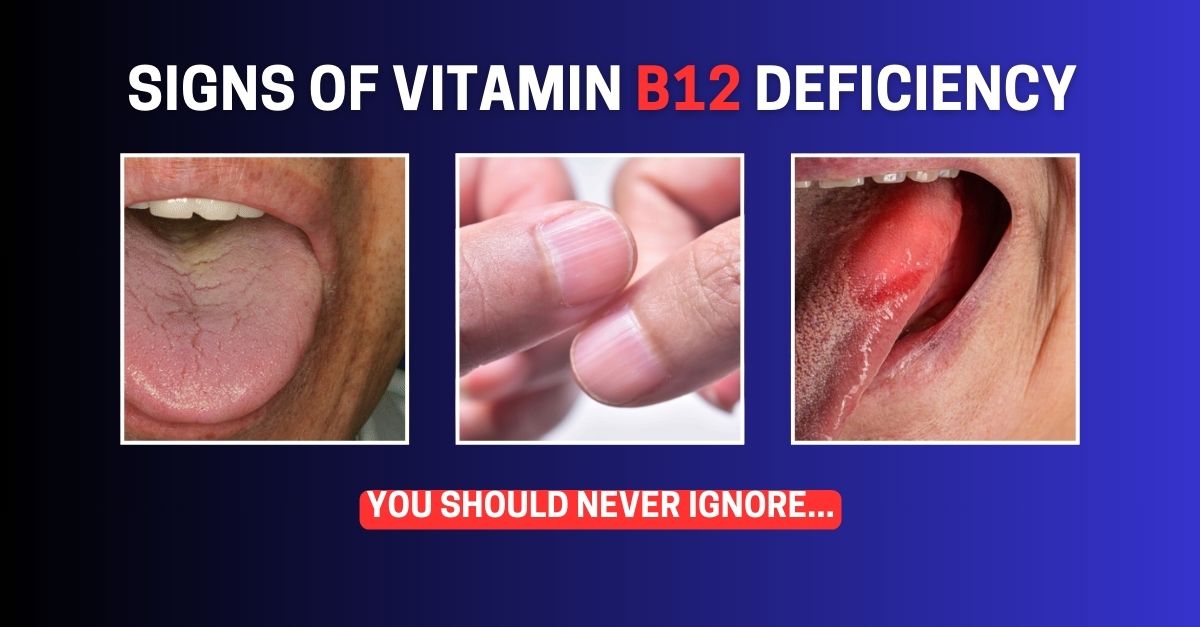
4. Nail and Mouth Issues
Vitamin B12 deficiency can also manifest through changes in your nails and oral health. Brittle or spoon-shaped nails (koilonychia) can indicate a lack of B12, as can frequent mouth ulcers. Additionally, a swollen or inflamed tongue (glossitis) is another sign of a deficiency. The tongue may appear red, smooth, or sore, which can make eating or speaking uncomfortable.
5. Unexplained Fatigue
Persistent tiredness, even without apparent cause, may point to a B12 deficiency. Reduced red blood cell production results in less oxygen circulating through the body, leading to fatigue.
6. Pale Skin
A pale complexion may be a result of the body’s attempt to compensate for reduced red blood cell production by increasing bilirubin levels, causing skin to lose its natural rosy hue.
7. Memory Problems
Vitamin B12 deficiency is also linked to memory issues, which can sometimes be mistaken for early signs of dementia or Alzheimer’s disease.
8. Tingling Sensations
Experiencing tingling or numbness in your hands or feet (also known as “pins and needles”) is another sign of B12 deficiency, as it affects the nerves.
Best Sources of Vitamin B12
If you suspect you’re not getting enough vitamin B12, here are some of the richest natural sources to add to your diet:
- Beef and chicken liver – 81 mg in 3 oz
- Salmon – 19.5 mg per filet (108 g)
- Herring – 18.7 mg per filet (143 g)
- Mackerel – 15.3 mg in 3 oz
- Sardines – 13.3 mg per cup
- Tuna – 9.3 mg in 3 oz
- Trout – 9.1 mg per filet
- Organic yogurt – 1.3 mg per container (plain Greek yogurt)
- Turkey – 1.1 mg in 3 oz
- Raw milk – 1 mg per cup
- Beef tenderloin – 0.9 mg in 3 oz
- Lamb – 0.8 mg in 3 oz
Additionally, vitamin B12 can be found in other non-vegan foods such as cheese, fortified cereals, and plant-based milk alternatives like almond or soy milk, as well as nutritional yeasts.
See also: 22 Warning Signs Your Body Needs Magnesium – And How to Fix It Fast!
In conclusion, vitamin B12 is essential for numerous bodily functions. Recognizing the signs of a deficiency early and making dietary changes can prevent serious health complications. Make sure you’re getting enough vitamin B12 to maintain your health and vitality.