Liver disease is a serious health condition that affects millions of people worldwide, often going unnoticed until significant damage has occurred. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and potential treatments is crucial for early detection and effective management.
Types of Liver Disease: What You Need to Know
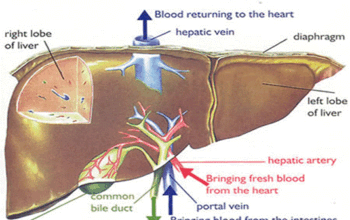
Liver disease encompasses a wide range of conditions that can impact liver function. Some of the most common types include:
- Hepatitis: A viral infection that causes liver inflammation, with multiple types including Hepatitis A, B, and C
- Fatty Liver Disease: Characterized by fat accumulation in liver cells, which can be alcoholic or non-alcoholic
- Cirrhosis: Advanced scarring of the liver tissue, often resulting from long-term liver damage
Recognizing the Symptoms of Liver Disease
Liver disease can be tricky to diagnose because symptoms often develop gradually and may initially seem mild or non-specific. However, several key indicators can signal potential liver problems:
Acute Liver Disease Symptoms
- Extreme fatigue and weakness
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dark-colored urine
- Pale or clay-colored stools
Chronic Liver Disease Symptoms
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent itching
- Swelling in the abdomen or legs
- Spider-like blood vessels on the skin
- Easy bruising or bleeding
Diagnostic Approaches
Medical professionals use several methods to diagnose liver disease:
Liver Function Tests
Blood tests can measure liver enzymes like ALT and AST, which indicate liver damage. Elevated levels might suggest inflammation or other liver issues.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
- Ultrasound
- CT scans
- MRI
- Liver biopsy for detailed tissue examination
Treatment and Management Strategies
Treatment depends on the specific type and stage of liver disease. Options include:
Medications
- Antiviral drugs for viral hepatitis
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Immunosuppressants for autoimmune conditions
Lifestyle Modifications
- Maintaining a healthy diet
- Regular exercise
- Alcohol cessation
- Weight management
Prevention is Key
While not all liver diseases can be prevented, several strategies can significantly reduce risk:
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis
- Practice safe sex
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Maintain a healthy body weight
- Avoid exposure to toxic chemicals
When to Seek Medical Help
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience persistent symptoms such as:
- Yellowing of skin or eyes
- Unexplained abdominal pain
- Chronic fatigue
- Unusual weight changes
Early detection and proactive management can make a significant difference in liver disease outcomes. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle are your best defense against serious liver complications.