Kidney disease is a serious health condition that affects millions of people worldwide, often progressing silently before causing significant damage. Understanding the early signs and taking proactive steps can make a crucial difference in managing and potentially slowing down the disease’s progression.
Understanding Kidney Disease: What You Need to Know
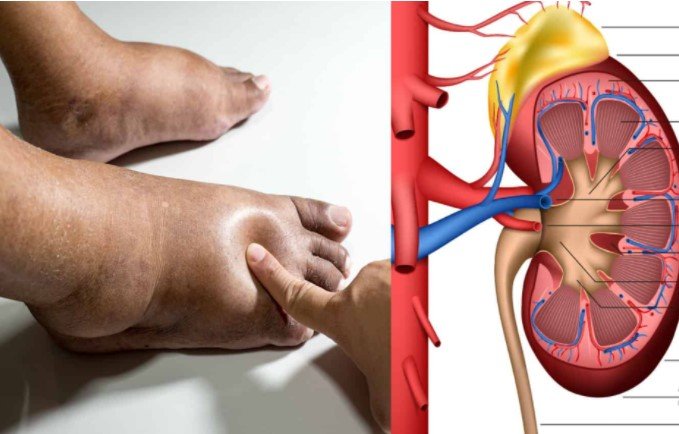
Kidneys are vital organs responsible for filtering waste, regulating blood pressure, and maintaining overall body balance. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) occurs when these essential organs gradually lose their ability to function effectively. Unlike acute kidney injury, CKD develops slowly over time, making early detection critical.
The human body has remarkable compensatory mechanisms, which means kidney function can decline significantly before noticeable symptoms emerge. In fact, individuals can lose up to 90% of their kidney function before experiencing severe symptoms.
Early Warning Signs: Recognizing the Subtle Signals
Early kidney disease often presents with subtle, easily overlooked symptoms. These include:
- Changes in Urination: Frequent urination, especially at night
- Swelling: Unexpected puffiness in feet, ankles, and hands
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and decreased energy levels
- Skin Changes: Dry, itchy skin with potential rashes
- Muscle Cramps: Unexplained muscle tension and cramping
Who is Most at Risk?
Certain groups are at higher risk of developing kidney disease:
- People with diabetes
- Individuals with hypertension
- Those with a family history of kidney disease
- Older adults
- African Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans
Diagnostic Approaches: Catching Kidney Disease Early
Modern medical diagnostics offer several methods to detect kidney disease in its early stages:
- Blood Tests: Measuring creatinine levels and glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
- Urine Tests: Checking for protein and blood in urine
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasounds to examine kidney structure
Prevention and Management Strategies
While some risk factors like age and genetics can’t be controlled, many lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce kidney disease risk:
- Maintain a balanced, nutritious diet
- Exercise regularly
- Stay hydrated
- Manage underlying conditions like diabetes and hypertension
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
Treatment Options
Early detection opens up multiple treatment possibilities:
- Medication to control underlying conditions
- Dietary modifications
- Lifestyle changes
- In advanced cases, dialysis or kidney transplant
When to See a Healthcare Professional
If you experience persistent symptoms or fall into high-risk categories, consult a healthcare provider. Regular check-ups and preventive screenings can catch kidney issues before they become severe.
Remember, your kidneys work tirelessly to keep your body healthy. By staying informed, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking early medical advice, you can protect these vital organs and ensure long-term wellness.