Skin cancer is a serious health concern that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding its early signs, risk factors, and prevention strategies can be life-saving. This comprehensive guide will help you recognize the key indicators of skin cancer and take proactive steps to protect your health.
Understanding Skin Cancer: What You Need to Know
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the United States, with over 9,500 people diagnosed every day. There are three primary types of skin cancer:
- Melanoma: The most dangerous form, which can spread quickly to other parts of the body
- Basal Cell Carcinoma: The most common type, typically developing in sun-exposed areas
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: The second most common type, often appearing on sun-exposed skin
Recognizing the Early Signs of Skin Cancer
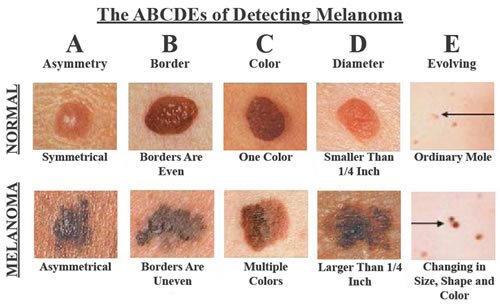
Early detection is crucial in successfully treating skin cancer. Dermatologists recommend using the ABCD rule when examining skin moles and lesions:
- A – Asymmetry: One half of the mole doesn’t match the other
- B – Border: Irregular, ragged, or blurred edges
- C – Color: Varied or inconsistent coloration
- D – Diameter: Larger than 6mm (about the size of a pencil eraser)
Additional warning signs include:
- New moles or growths
- Changes in existing moles
- Moles that itch, bleed, or become painful
- Sores that don’t heal
Understanding Risk Factors
Several factors can increase your risk of developing skin cancer:
- Prolonged exposure to UV radiation
- History of sunburns, especially during childhood
- Fair skin and light-colored hair
- Family history of skin cancer
- Weakened immune system
- Previous skin cancer diagnoses
Notably, people who use tanning beds before age 30 increase their melanoma risk by a staggering 75%.
Prevention Strategies
Protecting your skin is crucial in preventing skin cancer. Here are some key strategies:
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30
- Wear protective clothing and wide-brimmed hats
- Seek shade during peak sun hours (10 AM to 4 PM)
- Avoid tanning beds completely
- Conduct regular self-examinations
- Schedule annual skin checks with a dermatologist
Diagnosis and Treatment
If a suspicious mole or lesion is identified, a dermatologist will typically perform a biopsy. This involves removing a small sample of skin tissue for microscopic examination. If skin cancer is detected, treatment options depend on the type, size, location, and stage of the cancer.
Treatment may include:
- Surgical excision
- Mohs surgery (precise layer-by-layer removal)
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Immunotherapy
Promising Statistic: Early Detection Saves Lives
When detected early, the 5-year survival rate for melanoma is approximately 99%. This underscores the critical importance of regular skin examinations and being proactive about your skin health.
Remember, while this guide provides valuable information, it is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you notice any suspicious changes in your skin, consult a healthcare professional immediately.