Clogged arteries are a serious health condition that affects millions of people worldwide, silently increasing the risk of life-threatening cardiovascular events. Understanding the early warning symptoms, risk factors, and prevention strategies is crucial for maintaining heart health and potentially saving lives.
What Are Clogged Arteries?
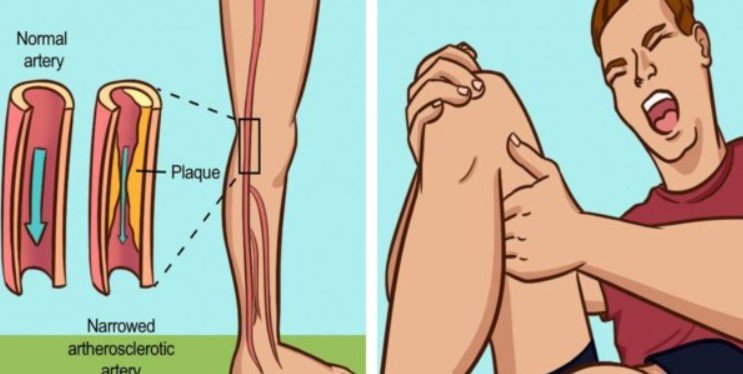
Atherosclerosis, commonly known as clogged arteries, is a condition where fatty deposits called plaque build up inside the arterial walls. These deposits gradually narrow and harden the arteries, restricting blood flow to vital organs like the heart and brain. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 16.5% of adults aged 20 and over have some form of cardiovascular disease.
Early Warning Symptoms of Clogged Arteries
Recognizing the early warning signs can be critical in preventing serious complications. Here are the most common symptoms to watch for:
Chest Pain and Angina
One of the most significant indicators of clogged arteries is chest pain or angina. This discomfort often feels like a squeezing or pressure in the chest and may radiate to the arm, neck, or jaw. Patients frequently describe it as a heavy weight or tightness that can occur during physical activity or emotional stress.
Shortness of Breath
Reduced blood flow can lead to difficulty breathing, especially during physical exertion. When arteries become blocked, the heart must work harder to pump blood, resulting in increased breathing difficulty and fatigue.
Pain or Numbness in the Legs
Peripheral artery disease can cause pain, numbness, or weakness in the legs, particularly during walking or exercise. This symptom, known as claudication, occurs when blocked arteries reduce blood flow to the lower extremities.
Risk Factors for Clogged Arteries
Several key risk factors contribute to the development of arterial blockage:
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol increase plaque buildup
- High Blood Pressure: Damages arterial walls and accelerates plaque formation
- Smoking: Tobacco use significantly increases the risk of arterial damage
- Diabetes: Increases inflammation and accelerates arterial deterioration
- Family History: Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in cardiovascular health
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Modern medical technology offers several diagnostic and treatment approaches for clogged arteries:
Diagnostic Tests
- Angiography
- Ultrasound imaging
- Blood tests to check cholesterol and triglyceride levels
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Treatment Strategies
Treatment typically involves a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle modifications:
- Medications: Statins, beta-blockers, and blood thinners
- Lifestyle Changes: Improved diet, regular exercise, stress management
- Surgical Options: Angioplasty, bypass surgery in severe cases
Prevention Strategies
Preventing clogged arteries is possible through proactive health management:
- Maintain a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Engage in regular physical activity (at least 150 minutes per week)
- Manage stress through meditation, yoga, or counseling
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption
- Regular health check-ups and monitoring of cholesterol and blood pressure
Conclusion
Clogged arteries are a serious health concern, but with early detection, proper management, and lifestyle modifications, individuals can significantly reduce their risk. Always consult healthcare professionals if you experience any warning symptoms or have concerns about your cardiovascular health.