Blood clots are a serious medical condition that can have life-threatening consequences if left undetected and untreated. Understanding the symptoms and risk factors is crucial for early identification and prompt medical intervention.
What is a Blood Clot?
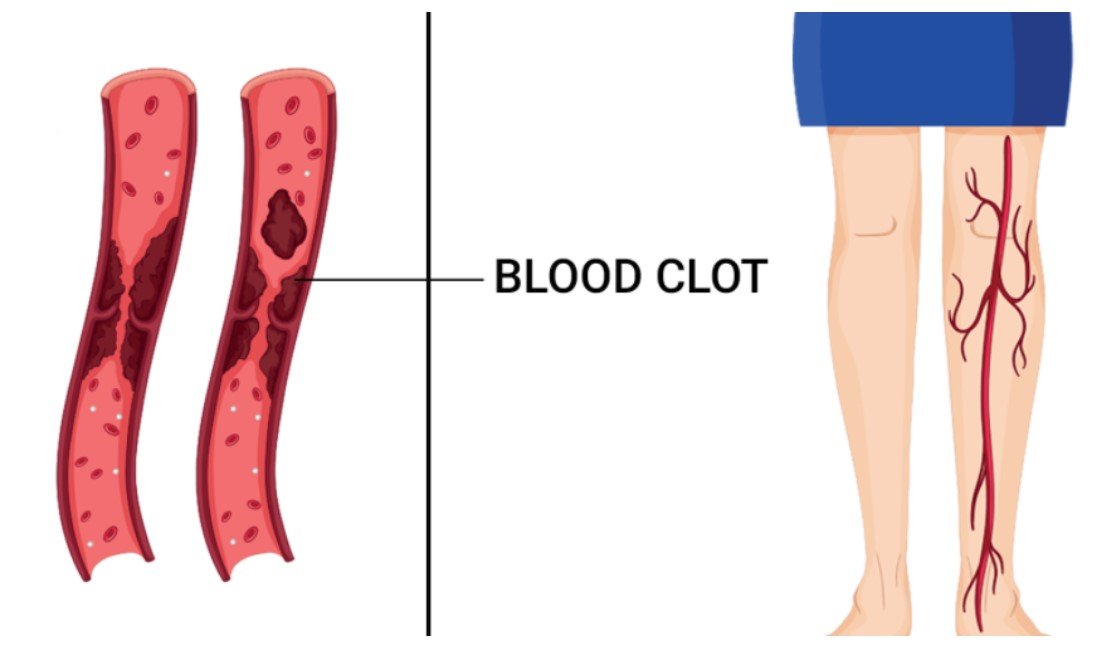
A blood clot, or thrombosis, occurs when blood transforms from a liquid to a gel-like or semisolid state. While blood clotting is a natural and necessary process to prevent excessive bleeding after an injury, problematic clots can form inside blood vessels without an obvious trigger, potentially blocking blood flow and causing significant health complications.
Types of Blood Clots
There are primarily two types of blood clots:
- Venous Thrombosis: Clots that form in veins, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Arterial Thrombosis: Clots that form in arteries, which can lead to heart attacks or strokes
Symptoms of Blood Clots in Different Body Parts
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Symptoms
DVT typically occurs in the legs and presents with several distinctive signs:
- Swelling in one or both legs
- Pain or tenderness in the leg
- Reddish or bluish skin discoloration
- Warm sensation in the affected area
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Symptoms
When a blood clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism, which presents with:
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breathing
- Rapid heart rate
- Coughing up blood
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded
Blood Clots in Other Areas
Clots can also form in other critical areas, each with unique symptoms:
- Kidneys: Blood in urine, severe abdominal pain, fever
- Heart: Severe chest pain, sweating, shortness of breath
- Brain: Sudden weakness, difficulty speaking, vision problems
Risk Factors
Some individuals are more susceptible to developing blood clots due to various factors:
- Prolonged immobility (e.g., long flights, bed rest)
- Recent surgery
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Hormonal birth control
- Pregnancy
- Family history of blood clots
- Certain chronic medical conditions
Diagnosis and Treatment
Healthcare professionals diagnose blood clots through various methods, including:
- Ultrasound imaging
- CT scans
- Blood tests
- Venography
Treatment typically involves anticoagulant medications (blood thinners) that prevent existing clots from growing and stop new clots from forming. In severe cases, thrombolytic drugs might be used to dissolve clots quickly.
Prevention Strategies
To reduce the risk of blood clots, consider these preventive measures:
- Stay physically active
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Stay hydrated
- Avoid prolonged sitting
- Wear compression stockings during long trips
- Quit smoking
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any symptoms suggestive of a blood clot, seek immediate medical help. Early detection and treatment can prevent serious complications and potentially save your life.
Remember, while this information is informative, it’s not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized guidance.