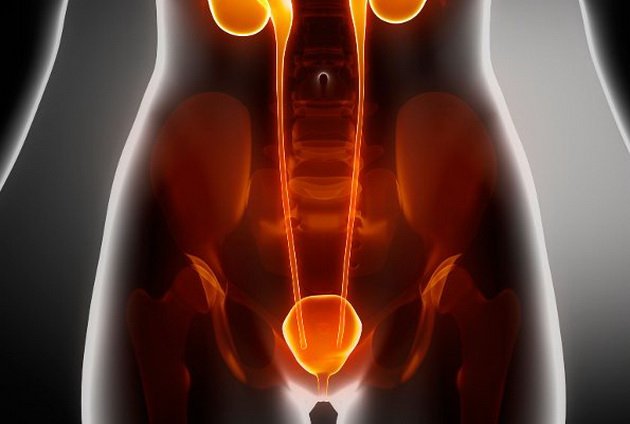
Kidney stones are a prevalent health issue affecting millions of people worldwide, causing significant discomfort and potential long-term complications. Nephrolithiasis, commonly known as kidney stone disease (KSD), is characterized by the formation of hard mineral deposits within the kidneys that can cause severe pain and urinary tract complications.
Understanding Kidney Stone Formation
Kidney stones develop when certain substances in urine, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid, become concentrated and crystallize. Several key risk factors contribute to stone formation:
- Low urine output
- Chronic dehydration
- Dietary imbalances
- Genetic predisposition
Research indicates that approximately 1 in 11 Americans will experience kidney stones during their lifetime, with recurrence rates as high as 50% within 10 years of the first episode. The economic burden of kidney stone treatment is estimated at billions of dollars annually.
Dietary Management Strategies
Effective dietary management plays a crucial role in preventing kidney stone formation. Key strategies include:
Optimal Fluid and Calcium Intake
Medical experts recommend consuming 2.5-3.0 liters of fluid daily to maintain proper hydration and promote adequate urine output. Calcium intake should be moderate, approximately 1000-1200 mg per day, consumed through dietary sources rather than supplements.
Sodium and Oxalate Regulation
Limiting sodium intake to 2-3.5 grams per day and reducing consumption of oxalate-rich foods can significantly decrease stone formation risk. Foods high in oxalates, such as spinach, rhubarb, and chocolate, should be consumed in moderation.
Lifestyle Modifications
Beyond dietary changes, several lifestyle factors can help prevent kidney stones:
- Maintaining a healthy Body Mass Index (BMI)
- Staying hydrated in high-temperature environments
- Avoiding cigarette smoking
- Regular physical activity
Natural Compounds and Medications
Certain natural bioactive compounds and medications can support kidney stone prevention:
Natural Compounds
Compounds like caffeine, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), and diosmin have shown potential in reducing stone formation through various mechanisms. These compounds can help regulate metabolic processes and reduce inflammation.
Pharmaceutical Interventions
Medications such as thiazides, alkaline citrate, and allopurinol can be prescribed to prevent stone recurrence. Clinical trials demonstrate their effectiveness in reducing stone formation rates by 50-70%.
The Role of Probiotics
Emerging research suggests that probiotics might play a significant role in kidney stone prevention. By maintaining gut health and potentially influencing mineral metabolism, probiotics could offer an innovative approach to stone prevention.
Comprehensive Prevention Approach
Preventing kidney stones requires a holistic strategy combining multiple interventions:
- Regular hydration
- Balanced diet
- Lifestyle modifications
- Medical supervision
- Potential supplementation
Conclusion
While kidney stones can be a challenging medical condition, proactive prevention through informed dietary choices, lifestyle modifications, and medical guidance can significantly reduce the risk of stone formation and recurrence.
Individuals concerned about kidney stones should consult healthcare professionals to develop personalized prevention strategies tailored to their specific health needs and risk factors.