Anemia is a common blood disorder affecting millions of people worldwide, characterized by a lack of healthy red blood cells to carry sufficient oxygen throughout the body. While medical treatment is crucial, dietary changes can play a significant role in managing and treating this condition. By understanding which foods can help combat anemia, individuals can take proactive steps toward improving their health and well-being.
Understanding Anemia: The Basics
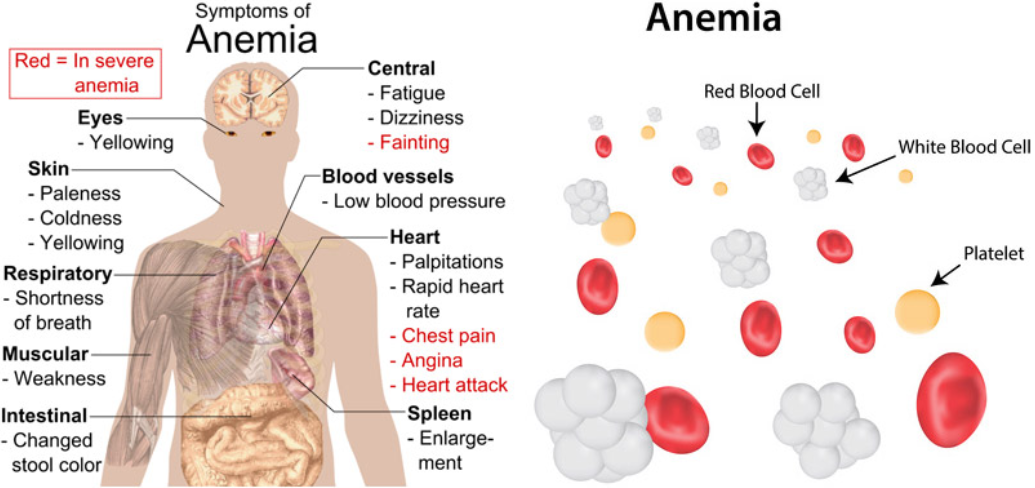
Anemia occurs when a person has fewer red blood cells than normal or lacks hemoglobin, the protein responsible for oxygen transportation. The condition can manifest through various symptoms, including:
- Persistent fatigue
- Weakness
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Irregular heartbeats
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
Iron-Rich Foods: Your Primary Defense
Iron is the most critical nutrient for combating anemia. The body requires iron to produce hemoglobin, which helps red blood cells transport oxygen effectively. To maximize iron intake, consider incorporating these foods into your diet:
Animal Sources of Iron
- Lean red meats
- Chicken and turkey
- Fish, especially salmon and tuna
- Organ meats like liver
Plant-Based Iron Sources
- Dark leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Beans and lentils
- Fortified cereals
- Tofu
- Dried fruits like raisins
Pro Tip: To enhance iron absorption, consume vitamin C-rich foods alongside iron sources. Citrus fruits, bell peppers, and strawberries can significantly improve iron uptake.
Other Essential Nutrients for Anemia Treatment
Folate-Rich Foods
Folate, or vitamin B9, is crucial in preventing and treating certain types of anemia. Key food sources include:
- Green leafy vegetables
- Legumes
- Nuts
- Fortified grains
Vitamin B12 Sources
Vitamin B12 is essential for red blood cell formation and energy production. Primary sources include:
- Dairy products
- Eggs
- Fish
- Meat
- Fortified plant-based milk
Additional Supportive Nutrients
Beyond iron, folate, and vitamin B12, other nutrients can support anemia management:
- Magnesium: Supports energy production and nerve function
- Found in whole grains
- Nuts and seeds
- Vitamin D: Supports overall immune health
- Fatty fish
- Fortified dairy products
- Egg yolks
Important Considerations
While dietary changes can significantly help manage anemia, they are not a complete substitute for medical treatment. Always consult healthcare professionals for comprehensive anemia management. Some individuals might require supplements or medical interventions depending on the underlying cause and severity of their condition.
By strategically incorporating these nutrient-rich foods into your diet, you can support your body’s ability to combat anemia, improve energy levels, and enhance overall health. Remember, consistency is key – make these dietary changes a sustainable part of your lifestyle for the best results.