Dehydration is a common yet often overlooked health issue that can have significant consequences on your overall well-being and body weight. While many people understand the basic importance of drinking water, few recognize the complex ways in which inadequate hydration can impact their physical and mental health.
Understanding Dehydration: More Than Just Feeling Thirsty
Dehydration occurs when your body loses more fluids than it takes in, disrupting the delicate balance of water and electrolytes necessary for optimal functioning. It’s not just about feeling thirsty – dehydration can manifest in subtle and serious ways that affect multiple body systems.
Types and Causes of Dehydration
Dehydration is typically categorized into three levels:
- Mild Dehydration: Minor fluid loss with minimal symptoms
- Moderate Dehydration: Noticeable fluid deficit causing more pronounced symptoms
- Severe Dehydration: Critical fluid loss requiring immediate medical intervention
Common causes include:
- Insufficient water intake
- Excessive sweating during physical activity
- Illness with fever, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Extreme weather conditions
- Certain medications
The Physical Impact of Dehydration
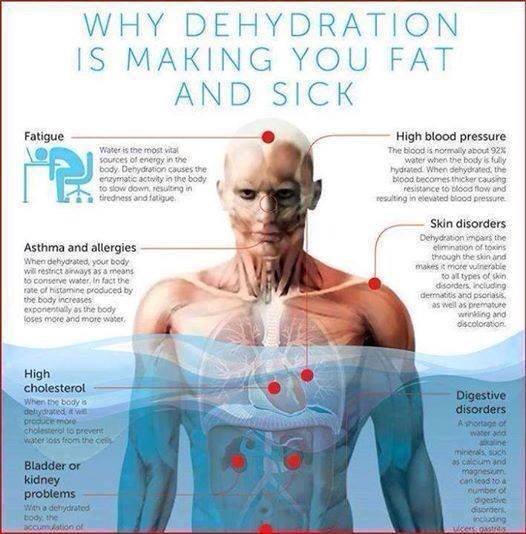
Dehydration doesn’t just make you feel uncomfortable – it can have profound effects on your body’s systems. Immediate symptoms often include headaches, dizziness, and fatigue. However, the long-term consequences can be even more serious.
Physiological Consequences
Chronic dehydration can lead to significant health issues, including:
- Reduced kidney function
- Increased blood pressure
- Impaired cognitive performance
- Compromised digestive health
- Decreased skin elasticity
Dehydration and Weight: The Unexpected Connection
Many people are surprised to learn that dehydration can directly impact weight management. When your body is dehydrated, it can:
- Slow down metabolism
- Decrease energy levels
- Increase water retention
- Trigger false hunger signals
Research suggests that individuals who are consistently well-hydrated tend to have more stable body weights and more efficient metabolic processes.
Prevention and Rehydration Strategies
Preventing dehydration requires a proactive approach. Experts recommend:
- Drinking 8-10 glasses of water daily
- Increasing water intake during physical activity
- Consuming water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables
- Monitoring urine color as a hydration indicator
Special Considerations
Some populations need extra attention to hydration:
- Athletes: Require more strategic hydration during training and competition
- Older Adults: Have decreased thirst perception and higher dehydration risks
- Children: More susceptible to rapid fluid loss
Quick Rehydration Techniques
When dehydration occurs, swift action is crucial. Consider these strategies:
- Drink water slowly and consistently
- Consume electrolyte-rich beverages
- Eat water-dense fruits like watermelon
- Avoid alcohol and excessive caffeine
Final Thoughts
Understanding and managing hydration is a critical aspect of maintaining overall health. By recognizing the signs of dehydration and implementing consistent hydration strategies, you can protect your body, optimize your weight management efforts, and enhance your overall well-being.
Remember, staying hydrated isn’t just about drinking water – it’s about maintaining a balanced approach to fluid intake that supports your body’s complex systems.